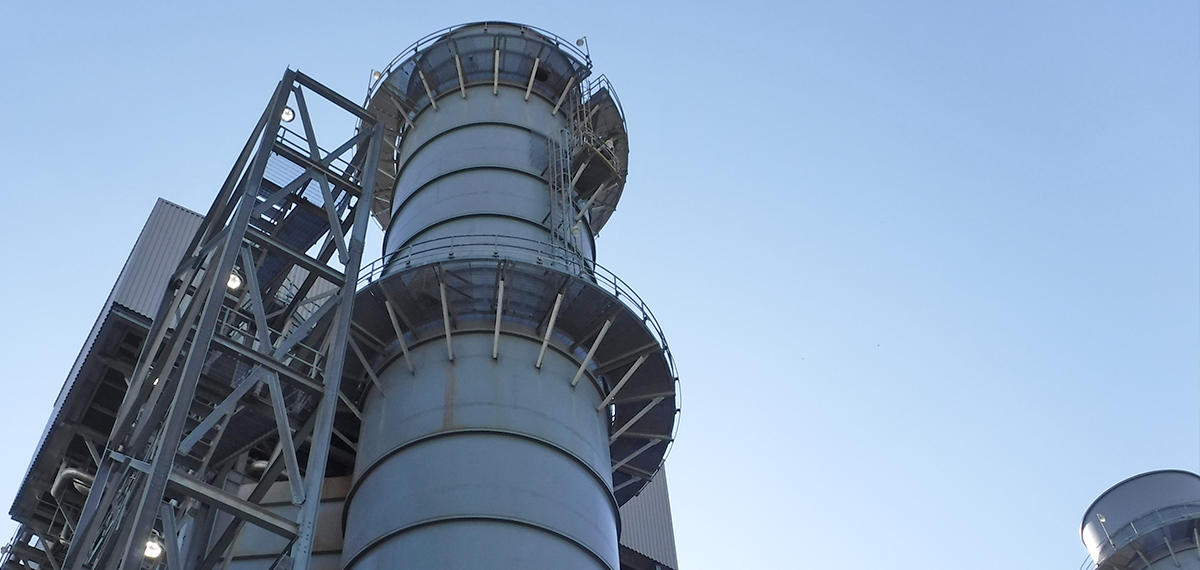
Power Generation
SUMMARY
TIME
1-2 days for a thorough inspection

COST
Only a small crew required

SAFETY
Track record for high level of safety standards
CONCERN
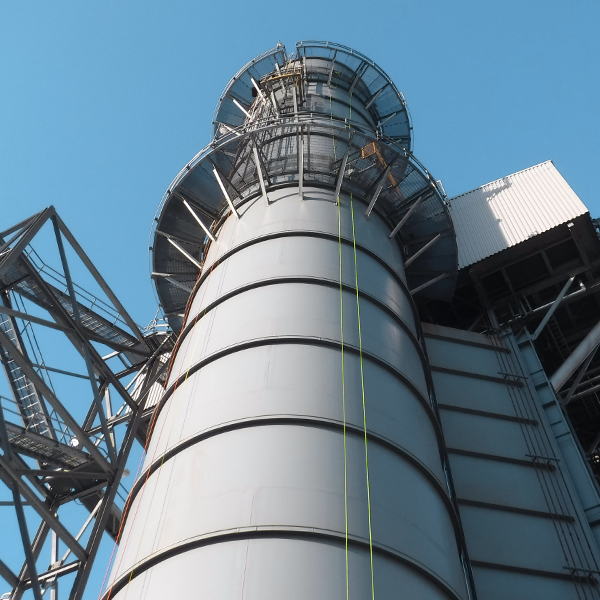

HRSG steel stack
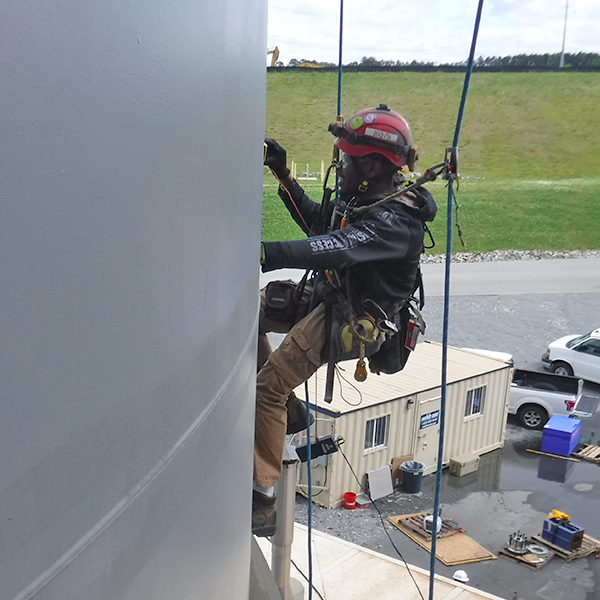

Utilizing rope access techniques
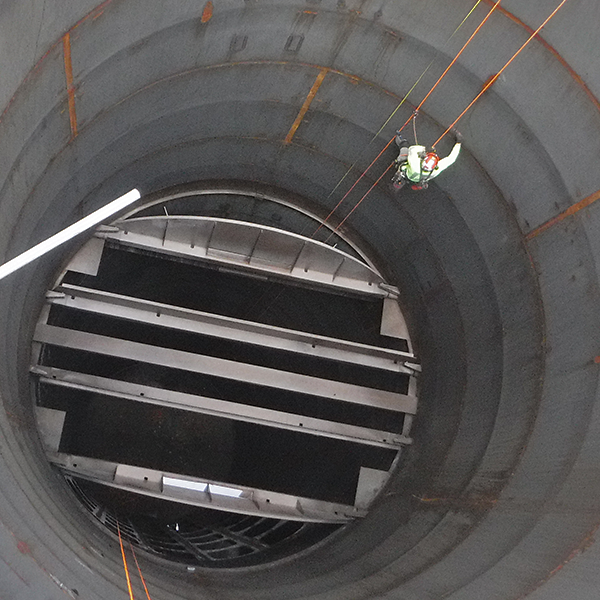

Interior inspection
ACCESS
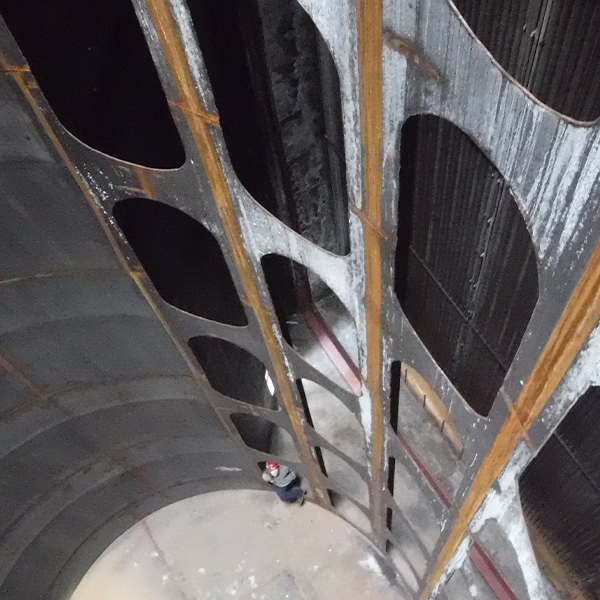

Interior inspection
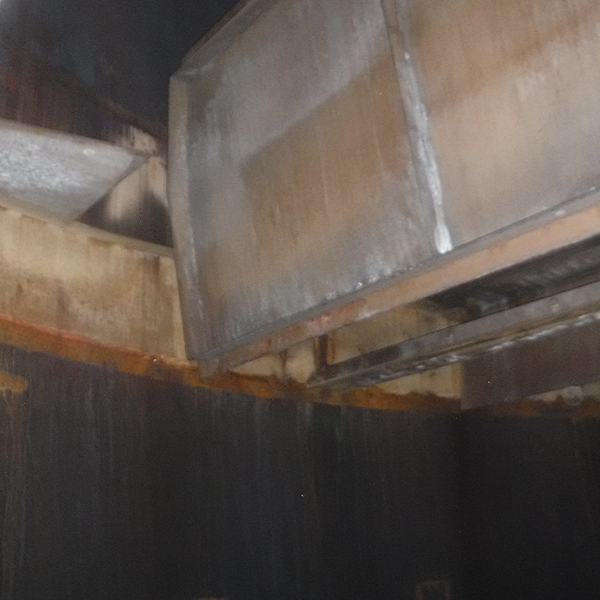

Stains on turning vanes
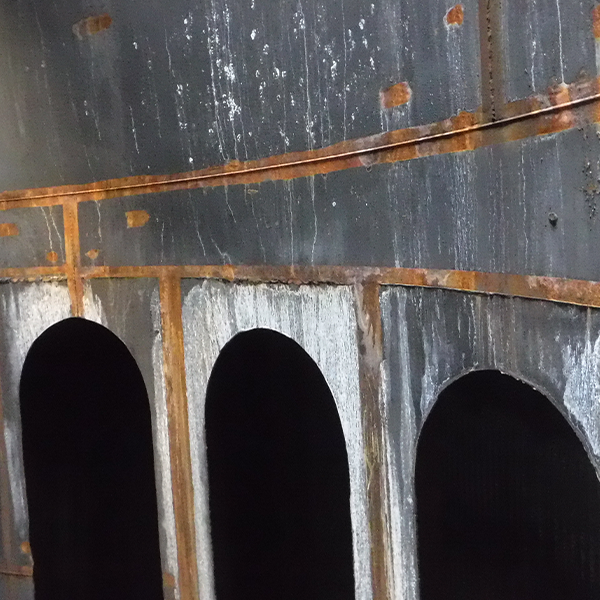

Oxidation stains and coating failure
SOLUTION
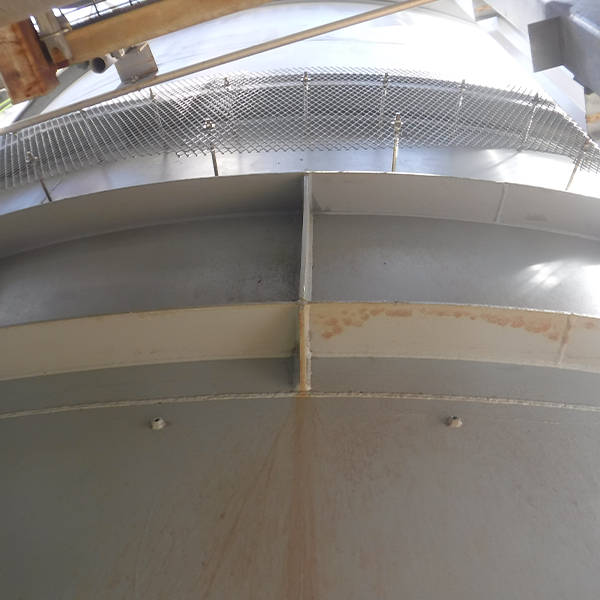

Exterior inspection
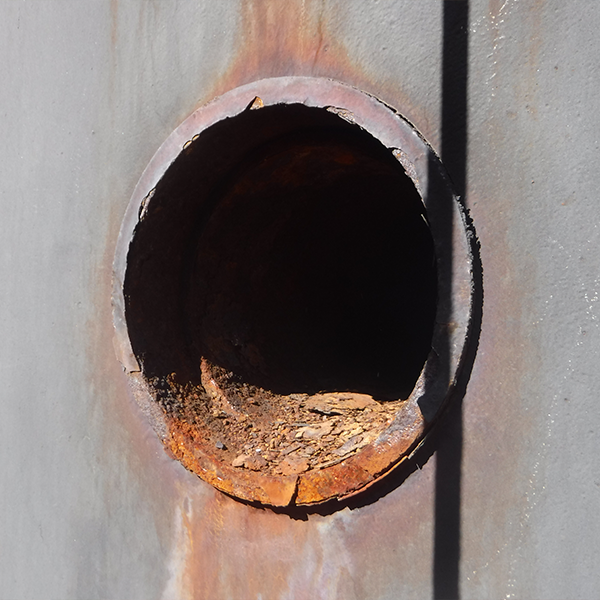

Debris in corroding test ports
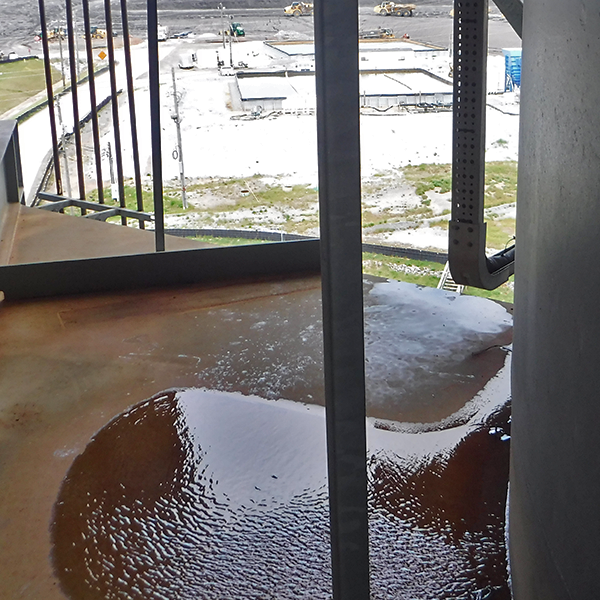

Water pooling can lead to damage
RESULTS

For additional information about our company and services we provide, please give us a call anytime
770-255-1313



